Designing The Ultimate Nutrition Plan For Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
TAKU

BY TAKU
Introduction:
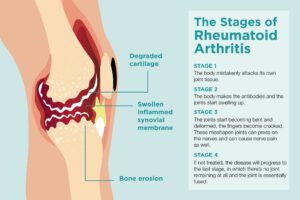
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and inflammation. While there is no definitive cure for RA, adopting a well-balanced nutrition plan can significantly help manage its symptoms and improve overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the best nutrition strategies to support individuals living with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Emphasize Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Focusing on an anti-inflammatory Personal Eating Plan can be beneficial for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Incorporate low sugar fruits and vegetables such as berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli, cauliflower). These foods are rich in antioxidants and phytochemicals that help combat inflammation. Don't forget to include other calcium-rich foods like leafy greens, raw dairy (if tolerated) to support bone health.

- Incorporate Nutrient-Rich Protein Sources: Ensure your nutrition plan includes a wide variety of nutrient-dense foods to provide essential vitamins and minerals. Include sources of high-quality proteins like grass fed beef, free range poultry, wild caught fish, pastured eggs. Additionally, include omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish (salmon, sardines) or plant-based sources like chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts, as they possess anti-inflammatory properties.

- Monitor Your Gut Health: Emerging research suggests a link between gut health and rheumatoid arthritis. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi can enhance the diversity of beneficial gut bacteria, potentially reducing inflammation. Additionally, including prebiotic foods like garlic, onions, and asparagus can promote the growth of healthy gut bacteria.

- Limit Trigger Foods: While certain foods can exacerbate inflammation, it is essential to identify personal trigger foods through trial and error. Common culprits include processed foods, refined sugars, saturated and trans fats, and excessive consumption of omega-6 fatty acids found in vegetable oils. It's crucial to listen to your body and observe how certain foods affect your RA symptoms. If necessary, work with a registered dietitian to identify and eliminate trigger foods.

- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing rheumatoid arthritis. Excess weight places additional strain on joints, worsening pain and inflammation. By incorporating a balanced nutrition plan and meaningful exercise such as safe efficient strength training, you can achieve and maintain a healthy weight, reducing the burden on your joints and improving overall well-being.

- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is often overlooked but plays a significant role in supporting joint health. Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to keep your body hydrated. Limit or avoid sugary beverages, as they may contribute to inflammation and weight gain.
Conclusion:
While nutrition alone cannot cure rheumatoid arthritis, adopting a well-balanced nutrition plan can significantly help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve overall quality of life. Emphasize anti-inflammatory foods, incorporate nutrient-rich options, monitor gut health, identify trigger foods, maintain a healthy weight, and stay hydrated. Remember, consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop a personalized nutrition plan that suits your specific needs and medical condition. By making informed dietary choices, you can take an active role in managing your rheumatoid arthritis and promoting overall well-being.
RA Research:
- A study published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition in 2017 investigated the effects of an anti-inflammatory diet on rheumatoid arthritis. The study found that participants following an anti-inflammatory diet experienced significant reductions in disease activity and improvements in symptoms compared to those following a typical Western diet. ______________________________________________________________________________
- In a randomized controlled trial published in the journal Arthritis Research & Therapy in 2018, researchers examined the impact of a Mediterranean diet on patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The study demonstrated that participants who followed the Mediterranean diet experienced improvements in disease activity, pain, and physical function, along with a reduction in inflammatory markers. ______________________________________________________________________________
- A systematic review and meta-analysis published in the journal Nutrition in 2018 analyzed the impact of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on rheumatoid arthritis. The review concluded that omega-3 fatty acid supplementation reduced disease activity and decreased the need for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. ______________________________________________________________________________
- In a study published in the journal Nutrition & Metabolism in 2018, researchers investigated the effects of a plant-based, gluten-free diet on patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The study found that participants following the plant-based, gluten-free diet experienced significant improvements in disease activity, pain, and quality of life compared to those following a typical Western diet. ______________________________________________________________________________
- A randomized controlled trial published in the journal Rheumatology International in 2019 examined the effects of a low-glycemic index diet on patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The study showed that participants following the low-glycemic index diet experienced improvements in disease activity, inflammation markers, and insulin resistance compared to those on a control diet. ______________________________________________________________________________
- A systematic review and meta-analysis published in the journal Frontiers in Nutrition in 2020 assessed the impact of probiotics on rheumatoid arthritis. The review found that probiotic supplementation significantly reduced disease activity and inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. ______________________________________________________________________________
- A study published in the journal Nutrition Research in 2021 investigated the effects of a Whole-Food, Mediterranean-style diet on patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The study demonstrated that participants following a Whole Food, Mediterranean-style diet experienced improvements in disease activity, pain, and physical function, along with a decrease in inflammatory markers.
TAKU's NOTE:
These studies provide compelling evidence supporting the effectiveness of anti-inflammatory nutrition plans, such as Whole Food based diets which prioritize high quality protein, avoid sugar and processed carbohydrates. Consider supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids and probiotics to assist in managing rheumatoid arthritis symptoms and reducing inflammation. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making any significant dietary changes to ensure it aligns with your individual needs and medical condition.
Recent Articles

Let’s set the record straight: losing your balance as you age is not inevitable. Despite what many believe, balance isn’t something you just “lose” over time like your hairline or your car keys. The truth is, most balance issues that show up later in life stem from something far more preventable—loss of strength and muscle mass.

Let me ask you something… If I told you that you could build strength, enhance performance, and reduce your risk of injury in less than one hour a week, would you believe me? No gimmicks. No magic pills. Just science-backed, time-tested strength training that works. Welcome to the world of High Intensity Training, or H.I.T. — the TNT Strength way.

When people think about injury risk during strength training, they often imagine something going wrong during the last rep of a hard set. That’s when you’re exhausted, your muscles are screaming, and the weight feels impossible. It seems like the danger would be highest right there, right?... Wrong.

At TNT Strength, safety isn’t just a priority—it’s the foundation of everything we do. Just like doctors take the Hippocratic Oath and vow to “first, do no harm,” we as strength coaches hold ourselves to a similar standard. Every rep, every session, every program we build is designed with that guiding principle in mind: help first, never harm.

Let’s set the record straight: losing your balance as you age is not inevitable. Despite what many believe, balance isn’t something you just “lose” over time like your hairline or your car keys. The truth is, most balance issues that show up later in life stem from something far more preventable—loss of strength and muscle mass.

Let me ask you something… If I told you that you could build strength, enhance performance, and reduce your risk of injury in less than one hour a week, would you believe me? No gimmicks. No magic pills. Just science-backed, time-tested strength training that works. Welcome to the world of High Intensity Training, or H.I.T. — the TNT Strength way.

When people think about injury risk during strength training, they often imagine something going wrong during the last rep of a hard set. That’s when you’re exhausted, your muscles are screaming, and the weight feels impossible. It seems like the danger would be highest right there, right?... Wrong.

At TNT Strength, safety isn’t just a priority—it’s the foundation of everything we do. Just like doctors take the Hippocratic Oath and vow to “first, do no harm,” we as strength coaches hold ourselves to a similar standard. Every rep, every session, every program we build is designed with that guiding principle in mind: help first, never harm.








